This type of bit is set with cube-shaped TSP elements. These elements are larger in size than the triangular TSP elements and as such, provide a greater degree of cutter protrusion. The setting density on a cubic-TSP core bit is somewhat lower than that of a comparably sized triangular-TSP core bit.
Cubic TSP bits are recommended for use in unconsolidated formations with a Mohs hardness in the range of 3 to 4. Typical formation types include (but are not limited to):
The dimensions of the TSP cutting elements that are used in this style of bit typically have a 5mm edge length
All cubic TSP core bits are provided with a semi-round (Style ‘W’) bit crown profile. Available waterway configurations include:
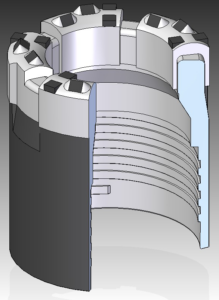 This waterway configuration feeds circulating fluid from the inside diameter across the bit face to the outside diameter through wide, wedge-shaped waterway canals that in most cases, include external junk slots. The wider canals and junk slots are necessary to promote the ejection of the larger cuttings that are typically produced by TSP bits. The TXW configuration is the standard for cubic-TSP core bits and is recommended for use in most applications. Higher circulation pump rates should be applied for effective performance.
This waterway configuration feeds circulating fluid from the inside diameter across the bit face to the outside diameter through wide, wedge-shaped waterway canals that in most cases, include external junk slots. The wider canals and junk slots are necessary to promote the ejection of the larger cuttings that are typically produced by TSP bits. The TXW configuration is the standard for cubic-TSP core bits and is recommended for use in most applications. Higher circulation pump rates should be applied for effective performance.
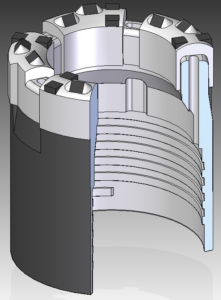 Recommended for use when drilling in relatively soft, unconsolidated formations and/or when using triple-tube wireline core barrel systems. The circulation fluid passes through slot-shaped ports that have been moulded into the bit face. This results in minimal core wash and thus reduces the potential for undesirable core sample erosion. By design, slot face discharge bits develop relatively low fluid pressure across the bit face, even when higher circulation rates are applied.
Recommended for use when drilling in relatively soft, unconsolidated formations and/or when using triple-tube wireline core barrel systems. The circulation fluid passes through slot-shaped ports that have been moulded into the bit face. This results in minimal core wash and thus reduces the potential for undesirable core sample erosion. By design, slot face discharge bits develop relatively low fluid pressure across the bit face, even when higher circulation rates are applied.